- Introduction
- dotnet tool Experience
- CZGL.SystemInfo
- SystemPlatformInfo
- ProcessInfo
- NetworkInfo
- DiskInfo
Introduction
CZGL.SystemInfo is a library that supports platforms such as Windows and Linux, capable of obtaining machine hardware information, collecting machine resource information, and monitoring process resources.
Without introducing extra dependencies, it utilizes the APIs of the .NET Runtime itself or calculates information to provide high-performance computing methods as well as caching to improve performance. It also provides a dotnet tool that can be used via the command line in the terminal.
Since this library is completely rewritten, it is entirely different from the old version of the API. Old version address:
Old version GitHub: https://github.com/whuanle/CZGL.SystemInfo/tree/0.1
Old version user guide: https://www.cnblogs.com/whuanle/p/12435413.html
Install by searching Nuget for CZGL.SystemInfo, the version is 1.0.
Each property and method in the library has been annotated with helpful comments and return examples.
CZGL.SystemInfo.Linux optimized certain parts of the code, with no other changes.
Windows can use System.Diagnostics.PerformanceCounter and System.Management.ManagementObjectSearcher to obtain performance counters and machine CPU models, disk serialization numbers, etc.
Platform differences make uniformity difficult, so calls to system-related APIs or command line operations are required to obtain the model serialization of certain hardware and resource information about processes, and customization is needed.
dotnet tool Experience
Currently, a simple dotnet tool has been created that requires no SDK and can be used with just the runtime.
Installation command:
dotnet tool install --global csys
# or
dotnet tool install --global csys --version 1.0.3You can invoke the tool using the following command: csys
Tool 'csys' (version '1.0.2') was successfully installed.If you are on Linux, you need to set the environment variable:
export PATH="$PATH:/home/{your_username}/.dotnet/tools"Once installed, enter the command to start the tool:
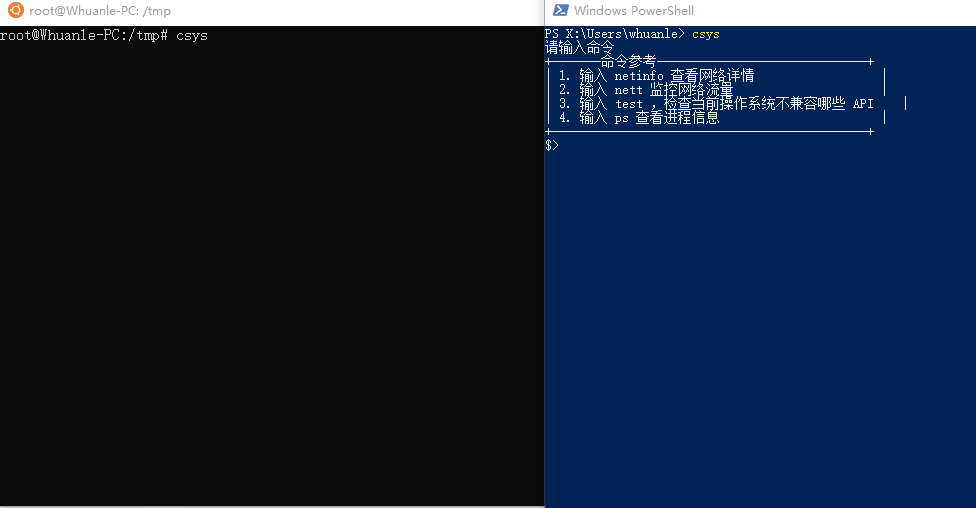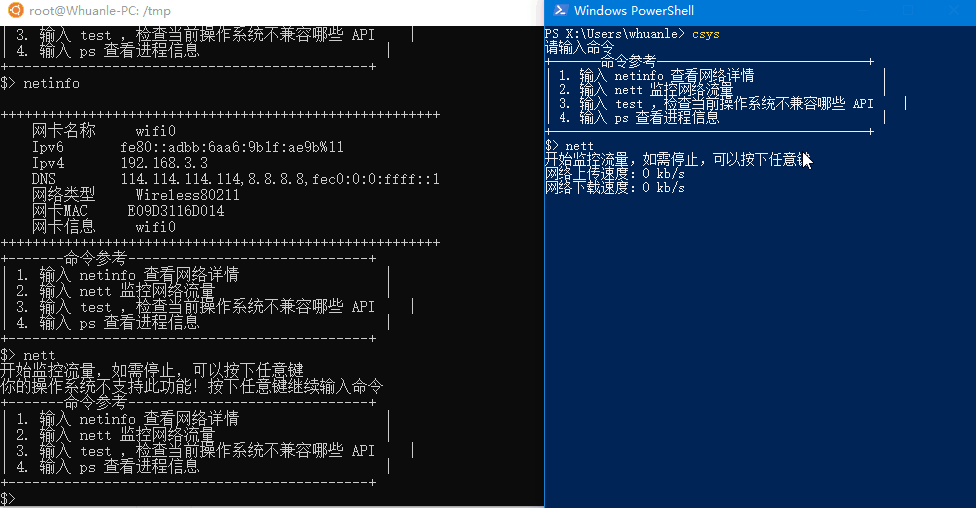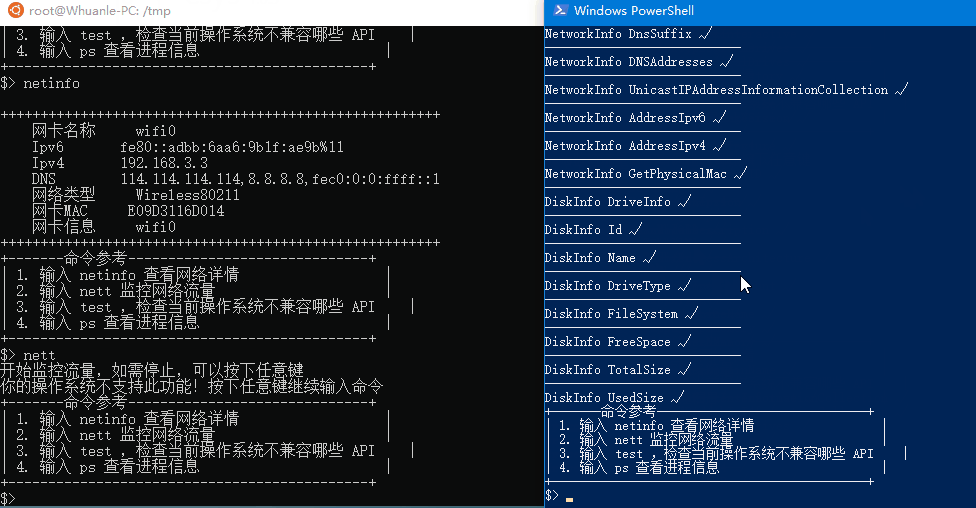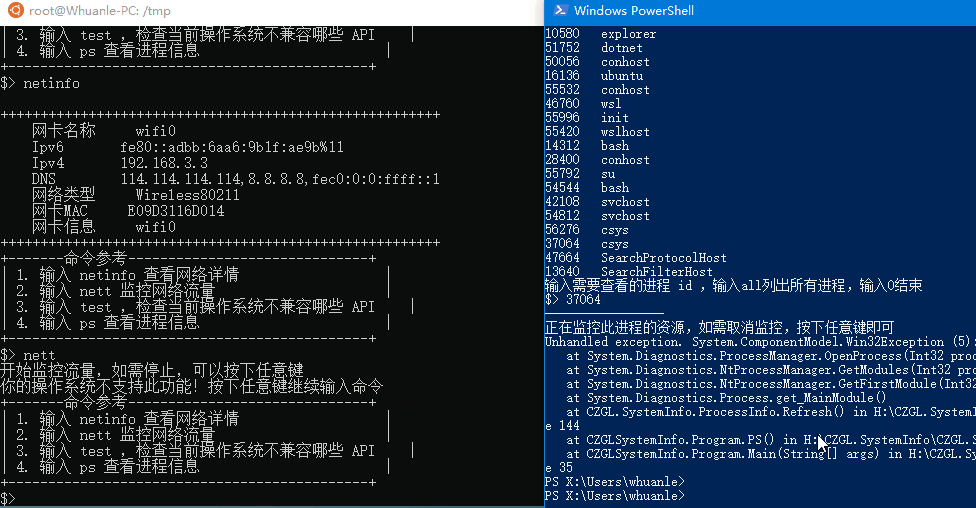
csysPlease enter a command
+-------Command Reference------------------------------+
| 1. Enter netinfo to view network details |
| 2. Enter nett to monitor network traffic |
| 3. Enter test, to check which APIs are incompatible with the current operating system |
| 4. Enter ps to view process information |
+---------------------------------------------+Note: You need to launch the program as a super administrator to use the ps feature;
GIF:
The tool has limited functionality, but if you are interested, you can download the Nuget package, which includes more features.
CZGL.SystemInfo
CZGL.SystemInfo currently has four classes: DiskInfo, NetworkInfo, ProcessInfo, SystemPlatformInfo, which will be introduced one by one.
To avoid resource waste, some properties of DiskInfo, NetworkInfo, and ProcessInfo use lazy loading, so they do not consume performance if this API is not used.
Install-Package CZGL.SystemInfo -Version 1.0.1SystemPlatformInfo
This is a static class that can retrieve runtime environment information and limited hardware information, all of which are determined before the program starts.
Its API description and example data are as follows:
| Property | Description | Windows Example | Linux Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| FrameworkDescription | Framework platform (.NET Core, Mono, etc.) information | .NET Core 3.1.9 | .NET Core 3.1.9 |
| FrameworkVersion | Runtime information version | 3.1.9 | 3.1.9 |
| OSArchitecture | Operating system platform architecture | X64 | X64 |
| OSPlatformID | Get the type of operating system | Win32NT | Unix |
| OSVersion | Operating system kernel version | Microsoft Windows NT 6.2.9200.0 | Unix 4.4.0.19041 |
| OSDescription | Operating system version description | Microsoft Windows 10.0.19041 | Linux 4.4.0-19041-Microsoft #488-Microsoft Mon Sep 01 13:43:00 PST 2020 |
| ProcessArchitecture | This process's architecture | X64 | X64 |
| ProcessorCount | Number of processors on the current machine | 8 | 8 |
| MachineName | Machine name | dell-PC | dell-PC |
| UserName | Current user name logged into this system | dell | dell |
| UserDomainName | User network domain name | dell-PC | dell-PC |
| IsUserInteractive | Whether it is running in interactive mode | True | True |
| GetLogicalDrives | List of disks and partitions in the system | D:\, E:\, F:\, G:\, H:\, J:\, X:|/, /dev, /sys, /proc, /dev/pts, /run, /run/lock, /run/shm | |
| SystemDirectory | Full path of the system root directory | X:\WINDOWS\system32 | |
| MemoryPageSize | Number of bytes per page of memory in the operating system | 4096 | 4096 |
The API of SystemPlatformInfo has no cross-platform compatibility issues and can be used confidently.
Demo:
System platform information:
Running framework : .NET Core 3.1.0
Operating system : Microsoft Windows 10.0.17763
Operating system version : Microsoft Windows NT 6.2.9200.0
Platform architecture : X64
Machine name : aaaa-PC
Current associated username : aaa
User network domain name : aaa-PC
System uptime (milliseconds) : 3227500
Web program core framework version : 3.1.0
Is it running in interactive mode? : True
Partition disks : D:, E:, F:, G:, H:, X:
System directory : X:\windows\system32
Current process's used physical memory : 20020
Current process's consumed CPU time : 328.125
All system processes various used memory : System.Collections.Generic.KeyValuePair`2[System.String,System.Int64][]
System used memory : 5988340
VisualStudioVersion : 16.0
ProcessInfo
You need to launch the program as a super administrator to use this feature;
Records resource data of the operating system at a certain moment. When using this API, you should note that monitoring and refreshing information will consume some performance resources.
By using two static methods, you can obtain the system's list of processes:
Dictionary<int,string> value = ProcessInfo.GetProcessList();
ProcessInfo[] value = ProcessInfo.GetProcesses();Or get a specified process by ID:
ProcessInfo value = ProcessInfo.GetProcess(666);After obtaining the ProcessInfo object, you must use the Refresh() method to refresh and capture current process state information to obtain the data.
For example:
ProcessInfo thisProcess = ProcessInfo.GetCurrentProcess(); // Get the current process's ProcessInfo object
thisProcess.Refresh();Information is not dynamic, and it captures the process state data at a certain point in time. Therefore, if dynamic updates are needed, it is required to execute the .Refresh() method again.
ProcessInfo can obtain how much memory and CPU time a process has used, but it cannot obtain this process's physical memory usage rate and CPU usage rate. If you wish to obtain the usage ratio, you need to call the operating system API or use other libraries from the operating system, such as WMI on Windows.
If you want to get the CPU consumption ratio of a process, you can use the static method:
decimal value = ProcessInfo.GetCpuPercentage(666);This refreshes roughly every 2 seconds, so do not wait indefinitely for this API to return data; this API is suitable for isolated calculations and not for integration with other data. The CPU percentage monitored by this API is not very accurate.
It's indeed difficult to capture CPU performance, and you can refer to the paper:
Continuously refreshing CPU data:
while (true)
{
var tmp = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
var process = ProcessInfo.GetProcess(tmp);
process.Refresh(); // Refresh process data
var cpu = ProcessInfo.GetCpuPercentage(process.ProcessId);
Console.WriteLine($"Process {process.ProcessName} CPU: {cpu * 100}%");
}Memory Monitoring
The value returned by the PhysicalUsedMemory property represents the current size of the pageable system memory used by the process (in bytes). System memory is the physical memory being used by the operating system, divided into pageable and non-pageable pools. When non-pageable memory is unused, it can be transferred to the virtual memory paging file on the disk.
| Property Name | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| PhysicalUsedMemory | Number of bytes of physical memory used | 17498112 |
NetworkInfo
NetworkInfo can retrieve network interface information.
NetworkInfo.GetNetworkInfo() can obtain the preferred network device that your computer is currently using to connect to the internet.
For example, if you are using Wi-Fi, it will retrieve the wireless network card; if you are using a wired connection, it will retrieve the Ethernet card.
API usage example:
var info = NetworkInfo.GetNetworkInfo();
Console.WriteLine("\r\n+++++++++++");
Console.WriteLine($" Network Card Name {info.Name}");
Console.WriteLine($" Network Link Speed {info.Speed / 1000 / 1000} Mbps");
Console.WriteLine($" Ipv6 {info.AddressIpv6.ToString()}");
Console.WriteLine($" Ipv4 {info.AddressIpv4.ToString()}");
Console.WriteLine($" DNS {string.Join(',', info.DNSAddresses.Select(x => x.ToString()).ToArray())}");
Console.WriteLine($" Upload Traffic Stats {info.SendLength / 1024 / 1024} MB");
Console.WriteLine($" Download Traffic Stats {info.ReceivedLength / 1024 / 1024} MB");
Console.WriteLine($" Network Type {info.NetworkType}");
Console.WriteLine($" Network Card MAC {info.Mac}");
Console.WriteLine($" Network Card Info {info.Trademark}");The Status property can be used to get the status of the network card, described in the following enumeration:
| Dormant | 5 | The network interface is not in a state of transferring packets; it is waiting for an external event. |
|---|---|---|
| Down | 2 | The network interface cannot transfer packets. |
| LowerLayerDown | 7 | The network interface cannot transfer packets because it runs over one or more other interfaces, and at least one of these "lower layer" interfaces is shut down. |
| NotPresent | 6 | The network interface cannot transfer packets due to missing components (usually hardware components). |
| Testing | 3 | The network interface is running tests. |
| Unknown | 4 | The status of the network interface is unknown. |
| Up | 1 | The network interface is operational and can transfer packets. |
NetworkType can be used to obtain the type of network card interface, with many enumerations available; for details please refer to:
Typically, network monitoring is done to check the network's integrity at a moment and to monitor traffic.
NetworkInfo.IsAvailable static property can check if the current machine can connect to the internet. The qualifying network card must be capable of transmitting packets and cannot be a local loopback address. If you are within an internal network, you may not need this API and can ping other machines in the internal network instead to ensure connectivity.
How to use real-time monitoring of network speed:
var info = NetworkInfo.GetNetworkInfo();
while (true)
{
var tmp = info.GetInternetSpeed(1000);
Console.WriteLine($"Network upload speed: {tmp.Send / 1024} kb/s");
Console.WriteLine($"Network download speed: {tmp.Received / 1024} kb/s");
Thread.Sleep(500);
}(int Received, int Send) GetInternetSpeed(int Milliseconds) method can monitor the amount of network transmission data, generally set with a time of 1000 ms.
Received is the download traffic
Send is the upload trafficGenerally speaking, a computer only has one network card connecting to the internet, so you can use:
static (int Received, int send) GetNowInternetSpeed(int Milliseconds)This will automatically find the network card that the computer is using to access the internet and record the traffic size.
There is also a Speed property to query the maximum supported speed of the network card.
If it is -1, it means that the link speed of this network card cannot be obtained; for example, 270_000_000 indicates a link speed of 270MB (generally refers to a 300M network card). A gigabit network card has a speed of 1000_000_000 (1000M).
Other APIs will not be introduced here.
Directly reflect and check:
NetworkInterface System.Net.NetworkInformation.SystemNetworkInterface
Id {43538D18-BB0E-4CE2-8F66-613FAC9467BD}
Mac E09D3116D014
Name WLAN
Trademark Intel(R) Centrino(R) Advanced-N 6205
PhysicalMac E09D3116D014
Status Up
NetworkType Wireless80211
Statistics System.Net.NetworkInformation.SystemIPInterfaceStatistics
Ipv4Statistics System.Net.NetworkInformation.SystemIPv4InterfaceStatistics
ReceivedLength 103449771
ReceivedLengthIpv4 103449771
SendLength 23753785
SendLengthIpv4 23753785
IsAvailable True
Speed 300000000
IsSupportIpv4 True
IsSupportIpv6 True
DnsSuffix
DNSAddresses System.Net.NetworkInformation.InternalIPAddressCollection
UnicastIPAddressInformationCollection System.Net.NetworkInformation.UnicastIPAddressInformationCollection
AddressIpv6 fe90::adbb:6aa1:2b1f:ae9b%11
AddressIpv4 192.168.3.3
GetPhysicalMac E69D3116D514Note that due to some APIs, the environment differences under Linux are quite large. It is recommended to use the csys tool's test command to check which APIs can be used in this Linux environment.
DiskInfo
There isn't much information that DiskInfo can retrieve.
You can use static methods to get all disk's DiskInfo objects:
DiskInfo.GetDisks()Directly reflect and view:
DriveInfo F:\
Id F:\
Name F:\
DriveType Fixed
FileSystem NTFS
FreeSpace 76498378752
TotalSize 112718770176
UsedSize 36220391424Linux
Search for CZGL.SystemInfo.Linux in Nuget and install it.
In this library, Linux resource information includes process metrics, memory metrics, CPU metrics, virtual memory metrics, and various process running information metrics.
To obtain it, you need to instantiate DynamicInfo.
There are 5 objects used to map the corresponding information.
Tasks: Used to count the number of processes and the number of processes in different states.
CpuState: CPU usage and various loading information of the CPU.
Mem: Physical memory and cache usage.
Swap: Virtual memory usage.
PidInfo: Resource usage information of a process.
They all have an IsSuccess property to determine whether Linux information can be retrieved normally.
Instantiate to obtain objects
DynamicInfo info = new DynamicInfo();Direct Usage
You can obtain the corresponding objects through methods.
var item = info.GetTasks();
Console.WriteLine("Total number of processes in the system :" + item.Total);
Console.WriteLine("Number of processes currently running :" + item.Running); Console.WriteLine(" ProcessId Process Name Owner User Optimization Level Priority Level Virtual Memory Physical Memory Shared Memory Process Status CPU Usage (%) Memory Usage (%) ");Output
Process Statistics:
Total : 93
Running : 1
Sleeping : 59
Stopped : 0
Zombie : 0
CPU Resource Statistics:
UserSpace : 1
Sysctl : 0.6
NI : 0
Idolt : 98.3
WaitIO : 0.1
HardwareIRQ : 0
SoftwareInterrupts : 0
Memory Statistics:
Total : 1009048
Used : 334040
Free : 85408
Buffers : 589600
CanUsed : 675008
Get Virtual Memory Statistics:
Total : 0
Used : 0
Free : 0
AvailMem : 505744

文章评论