package main
import (
"fmt"
"os"
"os/signal"
)
func main() {
// Set up channel on which to send signal notifications.
// We must use a buffered channel or risk missing the signal
// if we're not ready to receive when the signal is sent.
c := make(chan os.Signal, 1)
signal.Notify(c, os.Interrupt)
// Block until a signal is received.
s := <-c
fmt.Println("Got signal:", s)
}
The definition of the Notify function is as follows:
func Notify(c chan<- os.Signal, sig ...os.Signal)
os.Signal represents signals, and there are various kinds of signals, such as Interrupt and Kill, so it needs to be received via a channel to avoid losing signals.
c := make(chan os.Signal, 1)
Then listen for types of signals:
signal.Notify(c, os.Interrupt, os.Kill)
os.Interrupt denotes an interrupt;
os.Kill denotes a kill;
Under normal circumstances, the process is terminated when Ctrl+C is pressed. However, if it subscribes to signals, it can continue running without stopping.
The following example can receive two signals and perform some operations before exiting the process:
package main
import (
"fmt"
"os"
"os/signal"
)
func main() {
ci := make(chan os.Signal, 1)
ck := make(chan os.Signal, 1)
sleep := make(chan bool, 1)
signal.Notify(ci, os.Interrupt)
signal.Notify(ck, os.Kill)
go interrupt(ci, sleep)
go kill(ck, sleep)
<-sleep
}
func interrupt(ci chan os.Signal, sleep chan bool) {
s := <-ci
fmt.Println("Process interrupted:", s)
sleep <- true
}
func kill(ck chan os.Signal, sleep chan bool) {
s := <-ck
fmt.Println("Process killed", s)
sleep <- true
}
Pressing Ctrl+C:
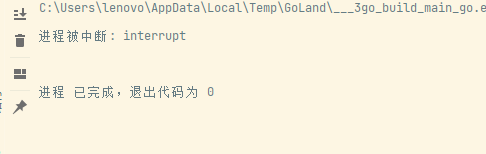
Of course, if it's a Kill signal, the process might be killed directly without any prompt.
Killing the process from the task manager:
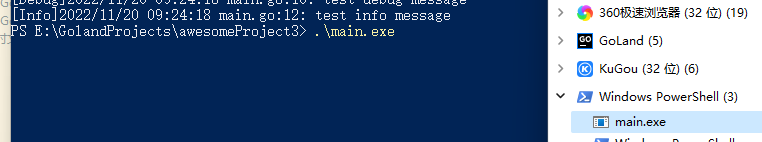
If it’s in Linux, there may still be some effect.
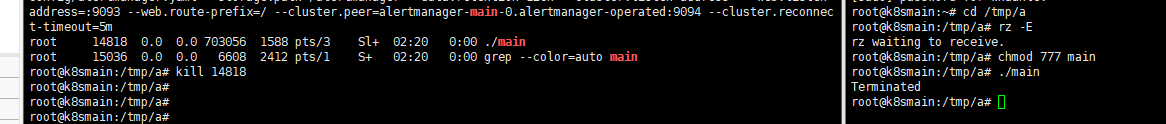
To stop listening for signals:
signal.Stop(ci)
Supported signals in Go:
| Signal Value | Value | Action | Description |
| :----------- | :------- | :----- | :----------------------------------------------------------- |
| SIGHUP | 1 | Term | Terminal control process ends (terminal connection disconnect)|
| SIGINT | 2 | Term | User sends INTR character (Ctrl+C) trigger |
| SIGQUIT | 3 | Core | User sends QUIT character (Ctrl+/) trigger |
| SIGILL | 4 | Core | Illegal instruction (program error, attempting to execute data segment, stack overflow, etc.) |
| SIGABRT | 6 | Core | Triggered by calling abort function |
| SIGFPE | 8 | Core | Arithmetic error (floating point error, division by zero, etc.) |
| SIGKILL | 9 | Term | Unconditionally terminate the program (cannot be caught, blocked, or ignored) |
| SIGSEGV | 11 | Core | Invalid memory access (attempting to access unowned memory, writing to read-only memory) |
| SIGPIPE | 13 | Term | Message pipe broken (FIFO/Socket communication when writing to a closed pipe) |
| SIGALRM | 14 | Term | Clock timer signal |
| SIGTERM | 15 | Term | End the program (can be caught, blocked, or ignored) |
| SIGUSR1 | 30,10,16 | Term | User defined |
| SIGUSR2 | 31,12,17 | Term | User defined |
| SIGCHLD | 20,17,18 | Ign | Child process ends (received by the parent process) |
| SIGCONT | 19,18,25 | Cont | Continue execution of a stopped process (cannot be blocked)|
| SIGSTOP | 17,19,23 | Stop | Stop the process (cannot be caught, blocked, or ignored) |
| SIGTSTP | 18,20,24 | Stop | Stop the process (can be caught, blocked, or ignored) |
| SIGTTIN | 21,21,26 | Stop | Triggered when a background program reads from the terminal |
| SIGTTOU | 22,22,27 | Stop | Triggered when a background program writes to the terminal |
Additional example:
package main
import (
"fmt"
"os"
"os/signal"
"syscall"
)
func main() {
SigChan := make(chan os.Signal, 1)
signal.Notify(SigChan, syscall.SIGHUP, syscall.SIGINT, syscall.SIGTERM, syscall.SIGQUIT)
sig := <-SigChan
switch sig {
case syscall.SIGHUP:
fmt.Println("\nSIGHUP signal generated")
case syscall.SIGINT:
fmt.Println("\nSIGINT signal generated")
case syscall.SIGTERM:
fmt.Println("\nSIGTERM signal generated")
case syscall.SIGQUIT:
fmt.Println("\nSIGQUIT signal generated")
default:
fmt.Println("\nUNKNOWN signal generated")
}
}

文章评论