这里是笔者在开发 MAUI 应用时踩的坑,以及一些笔记的汇总。
不得不说 MAUI 挺垃圾的。
如果不是 Mono 金玉在前,估计社区不会有多少人关注败絮 MAUI。
目前 .NET 已经升级到 7.0,但是 MAUI 还是一如既往的拉跨,如果开发过 MAUI,做过定制,自定义标题栏之类的,便会发现 MAUI 有多难受。
MAUI 不知道跟 UWP 有啥关系,但是 MAUI 很多东西感觉都是在延续 UWP 的设计,而且 MAUI 也很可能是下一个 UWP。
如果是 Windows 或者 Linux 桌面开发,建议 WPF 或 Avalonia, MAUI 真上不来台面,在 WPF 下面可以找到 好多 API ,但是 MAUI 都没有。。。
MAUI Windows 基于 WINUI 开发的,但是你按照 WINUI 去找资料,找到的东西 MAUI 又用不了。。。
这里笔者推荐一个好用的前端打包客户端工具 tauri ,tauri 是用 rust 实现的,然后可以结合其它前端框架开发应用。
其开发模式比 MAUI Blazor 好很多,开发体验也非常好,生成的软件体积也是出奇的小,而且生成的 app 自带安装界面,生成的程序就是已经打包好的,省得自己手动重新打包。
与其他桌面开相比, MAUI 真的非常臃肿,而且 MAUI Blazor 开发得真的不爽,包括 Visual Studio 本身的开发体验,框架本身的使用,以及 Blazor UI 框架,三个方面的体验都不够好。
能打的 Blazor 框架少,可以轻易扩展容易改造的 UI 框架更加少,目前发现能够使用的 Blazor 框架,比较好的有 MASA Blazor。
为什么这么说呢,首先是 Blazor 编写过程中,编辑器对 Razor 的支持不好,会经常出现没有语法提示,代码有错误但是编辑器没有提示,编辑器提示有错误实际上代码没有错误,等等。。。
其次,关于 MAUI 下 Blazor 的使用和 Blazor 框架的选型。在 MAUI 下使用 Blazor,如果使用第三方 UI 框架,引入之后,会发现其天然有一种封闭性。
如果使用纯前端框架开发,你会发现依赖引用关系很清晰,需要引用什么包,编译器会提示,编译时会提示。
而 Blazor 框架,很难知道里面用了哪些 js,Blazor dll 里面嵌套了 js 等文件,其本身就是一种封闭性,而关于内部的情况更加难以了解,出现了 Bug 调试难。
而且 Blazor 框架封装的代码 是 C# + js 写的,由于 C# 代码编译后无法修改,因此引用的 Blazor 库出问题时,难以查看调试源代码。还有,笔者从目前的 Blazor 框架中,看到了很多框架本身的代码非常臃肿,里面的设计和逻辑也不清晰,很多地方的代码限制了组件的扩展,开发者难以替换里面的实现。
过度设计也是一种毛病,因为为了支持而支持,为了灵活而灵活,过多的 API 设计和过多的参数呈现,过多的逻辑封装,实际上会让这些组件更加难用。
大多数 Blazor 框架都是个人仓库维护。而市面上精品的前端框架,几乎都是有大公司做背书,ViewJS、Ant Design 等,其框架本身有专业团队维护和大佬对框架进行设计,共同维护一个精品。
但是目前的 Blazor,我觉得,除了 MASA 做的,其它很难提得上 “精品”。
要夸 MASA ,笔者也是有理由的。
MASA 是真的用心在做生态,吸引了很多开发者和粉丝活跃参与,其开源共享精神值得敬佩。
如果你对 Blazor 有问题,对 MAUI 开发有问题,即使你用的不是 MASA 框架,你也可以到 MASA 群众提问,不会出现付费解答问题,也不会有人笑你菜,也不会有人笑你这都不懂。当然笔者并不是说开源项目付费解答有问题,我只是称赞 MASA 的开源精神。
期待 MASA 团队做出一个精品出来。
不过就目前来说, MAUI + Blazor 桌面开发,没啥优势。。。还会带来很多问题。。。
如果可以,不想再碰 MAUI。
下面来介绍一些 MAUI 的知识点。
窗口
首先,创建项目后, APP.cs 中,有个 Microsoft.Maui.Controls.Window。
MauiProgram.cs 中,有个 Microsoft.UI.Xaml.Window , 然后在 Windows 下 Microsoft.UI.Xaml.Window 是 Microsoft.Maui.MauiWinUIWindow, Microsoft.UI.Xaml.Window 多种平台统一的抽象。
然后 Microsoft.UI.Xaml.Window 可以获取一个 AppWindow。
AppWindow appWindow = nativeWindow.GetAppWindow()!;
MAUI 里面的 Window 类 API 很混乱,大多数是从 UWP 写法继承,然后有很多 API 是 UWP 有的,但是 MAUI 没有。
混乱。
如果自己写了一个页面,要弹出这个窗口页面,那么应该使用 Microsoft.Maui.Controls.Window ,但是自己写的页面是 ContentPage,并不是 Window。
因此并不能直接使用 Window,而是将 ContentPage 放到 Window 中,生成 Window 后再操作。
private Microsoft.Maui.Controls.Window BuildUpdateWindow(ContentPage updatePage)
{
Window window = new Window(updatePage);
window.Title = "更新通知";
return window;
}
然后弹出这个窗口。
Application.Current!.OpenWindow(updateWindow!);
如果要异步打开窗口,请使用 Application.Current!.Dispatcher.DispatchAsync。
await Application.Current!.Dispatcher.DispatchAsync(async () =>
{
try
{
Application.Current!.OpenWindow(updateWindow!);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Logger.LogError("无法启动更新窗口", ex);
}
});
如果想关闭所有窗口:
await Application.Current!.Dispatcher.DispatchAsync(async () =>
{
var windows = Application.Current!.Windows.ToArray();
foreach (var window in windows)
{
try
{
Application.Current.CloseWindow(window);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Debug.Assert(ex != null);
}
}
});
虽然你获得了 Microsoft.Maui.Controls.Window ,但是不能直接管理这个 Window,而是应该通过 Microsoft.UI.Xaml.Window,或 Microsoft.UI.Windowing.AppWindow 管理。
也就是在依赖注入里面的窗口生命周期管理里面写。
或者除非你可以拿到 AppWindow 实例。
遗憾的是,Microsoft.Maui.Controls.Window 转不了 Microsoft.UI.Xaml.Window 或 Microsoft.UI.Windowing.AppWindow。
你应该这样写:
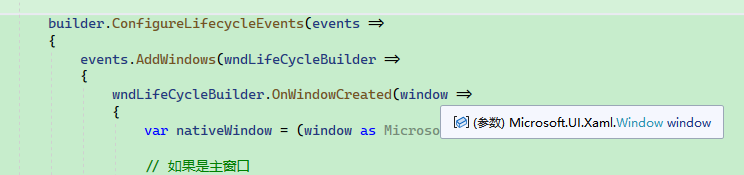
builder.ConfigureLifecycleEvents(events =>
{
events.AddWindows(wndLifeCycleBuilder =>
{
wndLifeCycleBuilder.OnWindowCreated(window =>
{
var nativeWindow = (window as Microsoft.Maui.MauiWinUIWindow)!;
... ...
})
.OnActivated((window, args) =>
{
})
.OnClosed((window, args) =>
{
});
});
});
private static void MainWindowCreated(MauiWinUIWindow nativeWindow)
{
const int width = 1440;
const int height = 900;
AppWindow appWindow = nativeWindow.GetAppWindow()!;
// 扩展标题栏,要自定义标题栏颜色,必须 true
nativeWindow.ExtendsContentIntoTitleBar = true;
// 这里必须设置为 Overlapped,之后窗口 Presenter 就是 OverlappedPresenter,便于控制
appWindow.SetPresenter(AppWindowPresenterKind.Overlapped);
//if (appWindow.Presenter is OverlappedPresenter p)
//{
// // p.SetBorderAndTitleBar(hasBorder: false, hasTitleBar: true);
//}
// 重新设置默认打开大小
appWindow.MoveAndResize(new RectInt32(1920 / 2 - width / 2, 1080 / 2 - height / 2, width, height));
// 窗口调整的各类事件
appWindow.Changed += (w, e) =>
{
// 位置发生变化
if (e.DidPositionChange)
{
}
if (e.DidPresenterChange) { }
// 大小发生变化
if (e.DidSizeChange) { }
if (e.DidVisibilityChange) { }
if (e.DidZOrderChange) { }
};
appWindow.Closing += async (w, e) =>
{
try
{
Environment.Exit(0);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
var log = AppHelpers.LoggerFactory.CreateLogger<AppWindow>();
log.LogError(ex, "Can't close WebHost");
ProcessManager.ReleaseLock();
}
finally
{
ProcessManager.ExitProcess(0);
}
};
appWindow.MoveInZOrderAtTop();
}
其次,你想直接获取当前的窗口实例,也是麻烦。
可以通过以下代码获取当前程序打开的所有窗口。
App.Current.Windows
Application.Current.Windows
如果你想获取当前正在使用或激活的窗口,笔者并不知道怎么通过里面的 API 获取。。。如果用 Win32 那么倒是可以。
问:有没有一种这样的 API 呢?
Current.GetWindos()
另外,MAUI 做不到自定义标题栏, 天王老子来了都不行。
你想给标题栏改个背景色,估计都得累死。
如果要修改窗口标题,只能在窗口创建时修改,也就是 Microsoft.Maui.Controls.Windows,用 Microsoft.UI.Xaml.Window,或 Microsoft.UI.Windowing.AppWindow 都改不了。
Microsoft.Maui.Controls.Window window = base.CreateWindow(activationState);
window.Title = Constants.Name;
如果要获取原生的 Window 句柄,可以使用:
var nativeWindow = mauiWindow.Handler.PlatformView;
IntPtr windowHandle = WinRT.Interop.WindowNative.GetWindowHandle(nativeWindow);
窗口管理
前面提到,想管理窗口,API 要用 Microsoft.UI.Xaml.Window,或 Microsoft.UI.Windowing.AppWindow 的。
有些地方只能用原生的 Window 窗口句柄,然后用 Win32 操作
自定义窗口生命周期时,一定要使用:
// 这里必须设置为 Overlapped,之后窗口 Presenter 就是 OverlappedPresenter,便于控制
appWindow.SetPresenter(AppWindowPresenterKind.Overlapped);
然后常用的窗口方法有:
/*
AppWindow 的 Presenter ,一定是 OverlappedPresenter
*/
public class WindowService : IWindowService
{
private readonly AppWindow _appWindow;
private readonly Window _window;
private WindowService(AppWindow appWindow, Window window)
{
_appWindow = appWindow;
_window = window;
}
// 检查当前窗口是否全屏
public bool FullScreenState
{
get
{
switch (_appWindow.Presenter)
{
case OverlappedPresenter p:return p.State == OverlappedPresenterState.Maximized;
case FullScreenPresenter p:return p.Kind == AppWindowPresenterKind.FullScreen;
case CompactOverlayPresenter p: return p.Kind == AppWindowPresenterKind.FullScreen;
case AppWindowPresenter p: return p.Kind == AppWindowPresenterKind.FullScreen;
default:return false;
}
}
}
// 让窗口全屏
public void FullScreen()
{
switch (_appWindow.Presenter)
{
case OverlappedPresenter overlappedPresenter:
overlappedPresenter.SetBorderAndTitleBar(true, true);
overlappedPresenter.Maximize();
break;
}
// 全屏时去掉任务栏
// _appWindow.SetPresenter(AppWindowPresenterKind.FullScreen);
}
// 退出全屏
public void ExitFullScreen()
{
switch (_appWindow.Presenter)
{
case OverlappedPresenter p: p.Restore();break;
default: _appWindow.SetPresenter(AppWindowPresenterKind.Default); break;
}
}
// 最小化到任务栏
public void Minmize()
{
#if WINDOWS
var mauiWindow = App.Current.Windows.First();
var nativeWindow = mauiWindow.Handler.PlatformView;
IntPtr windowHandle = WinRT.Interop.WindowNative.GetWindowHandle(nativeWindow);
PInvoke.User32.ShowWindow(windowHandle, PInvoke.User32.WindowShowStyle.SW_MINIMIZE);
#endif
}
/// <summary>
/// 激活当前窗口
/// </summary>
public void Active()
{
_appWindow.Show(true);
}
// 关闭窗口
public void Exit()
{
_window.Close();
}
public void SetSize(int _X, int _Y, int _Width, int _Height)
{
_appWindow.MoveAndResize(new RectInt32(_X, _Y, _Width, _Height));
}
public (int X, int Y) GetPosition()
{
var p = _appWindow.Position;
return (p.X, p.Y);
}
public (int X, int Y) Move(int x, int y)
{
_appWindow.Move(new PointInt32(x, y));
return GetPosition();
}
public (int Width, int Height, int ClientWidth, int ClientHeight) GetSize()
{
var size = _appWindow.Size;
var clientSize = _appWindow.ClientSize;
return (size.Width, size.Height, clientSize.Width, clientSize.Height);
}
public (PointInt32 Position, SizeInt32 Size, SizeInt32 ClientSize) GetAppSize()
{
return (_appWindow.Position, _appWindow.Size, _appWindow.ClientSize);
}
}
让窗口全屏有两种方法,一种是全屏时,窗口把任务栏吞了,真正意义上的的全屏,另一种是保留任务栏。
// 保留任务栏
switch (_appWindow.Presenter)
{
case OverlappedPresenter overlappedPresenter:
overlappedPresenter.SetBorderAndTitleBar(true, true);
overlappedPresenter.Maximize();
break;
}
// 全屏时去掉任务栏
// _appWindow.SetPresenter(AppWindowPresenterKind.FullScreen);
最小化只能通过 Win32 API 处理,你要先获取 Microsoft.Maui.Controls.Windows,然后转换为 Window 句柄。
var nativeWindow = mauiWindow.Handler.PlatformView;
IntPtr windowHandle = WinRT.Interop.WindowNative.GetWindowHandle(nativeWindow);
PInvoke.User32.ShowWindow(windowHandle, PInvoke.User32.WindowShowStyle.SW_MINIMIZE);
此时
Microsoft.UI.Xaml.Window,或Microsoft.UI.Windowing.AppWindow就用不上了。
前面提到,要使用 Microsoft.UI.Xaml.Window,或 Microsoft.UI.Windowing.AppWindow ,例如在 MauiProgram.cs 里面记录了窗口的事件,创建窗口时控制大小。
但是,窗口运行中,要设置窗口大小或限制大小,则是要通过 Microsoft.Maui.Controls.Windows。
例如,控制主窗口大小不能太小,不能被无限缩小,要在 APP.cs 中这样写:
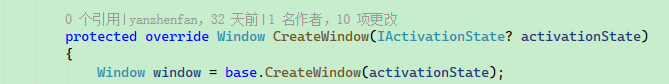
protected override Window CreateWindow(IActivationState? activationState)
{
Window window = base.CreateWindow(activationState);
window.Title ="窗口标题";
var minSize = GetMinSize();
window.MinimumWidth = minSize.MinWidth;
window.MinimumHeight = minSize.MinHeight;
// Give the Window time to resize
window.SizeChanged += (sender, e) =>
{
var minSize = GetMinSize();
window.MinimumWidth = minSize.MinWidth;
window.MinimumHeight = minSize.MinHeight;
};
//window.Created += (s, e) =>
//{
//};
//window.Stopped += (s, e) =>
//{
//};
return window;
(int MinWidth, int MinHeight) GetMinSize()
{
// 获取当前屏幕的长宽,用 X、Y 表示。
var x = PInvoke.User32.GetSystemMetrics(PInvoke.User32.SystemMetric.SM_CXFULLSCREEN);
var y = PInvoke.User32.GetSystemMetrics(PInvoke.User32.SystemMetric.SM_CYFULLSCREEN);
// 设置窗口最小值,可以按照比例计算,也可以直接设置固定大小
return (x / 3 * 2, y / 5 * 4);
}
}
PS,在 AppWindow 里面的事件做大小限制,是做不到的,这里主要是观察,想做窗口大小等限制是不行的。
// 窗口调整的各类事件
appWindow.Changed += (w, e) =>
{
// 位置发生变化
if (e.DidPositionChange)
{
}
if (e.DidPresenterChange) { }
// 大小发生变化
if (e.DidSizeChange) { }
if (e.DidVisibilityChange) { }
if (e.DidZOrderChange) { }
};
如何限制一次只能打开一个程序
场景,如果程序D 已被运行 进程 A,那么再次启动程序D 运行进程 B,B 会识别到已有相同的进程,此时 B 会将 A 窗口激活弹出来,然后 B 再退出。
这样不仅可以限制只能运行一个进程,而且可以让用户体验更加好。
锁可以使用 Mutex 来实现,在整个操作系统中,大家可以识别到同一个锁。
然后激活另一个窗口,可以使用 Win32。
// 进程管理器
internal static class ProcessManager
{
private static Mutex ProcessLock;
private static bool HasLock;
/// <summary>
/// 获取进程锁
/// </summary>
public static void GetProcessLock()
{
// 全局锁
ProcessLock = new Mutex(false, "Global\\" + "自定义锁名称", out HasLock);
if (!HasLock)
{
ActiveWindow();
Environment.Exit(0);
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 激活当前进程并将其窗口放到屏幕最前面
/// </summary>
public static void ActiveWindow()
{
string pName = Constants.Name;
Process[] temp = Process.GetProcessesByName(pName);
if (temp.Length > 0)
{
IntPtr handle = temp[0].MainWindowHandle;
SwitchToThisWindow(handle, true);
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 释放当前进程的锁
/// </summary>
/// <remarks>小心使用</remarks>
public static void ReleaseLock()
{
if (ProcessLock != null && HasLock)
{
ProcessLock.Dispose();
HasLock = false;
}
}
// 将另一个窗口激活放到前台。
// Win32 API
[DllImport("user32.dll")]
public static extern void SwitchToThisWindow(IntPtr hWnd, bool fAltTab);
}
然后在程序启动时使用。
MAUI 程序安装模式
如果直接使用原生的 MAUI 程序,安装时会特别麻烦,因为这种方式就是以前的 UWP。
因此,可以使用那种,不需要安装直接运行的方式。
但是这里我们要了解一下两种模式的区别。
如果使用原生 MAUI 模式,那么会被生成 Windows 应用市场应用,无论是发布、上架、安装,都是非常麻烦的。但是好在可以使用很多 Windows 应用的 API。
例如要获取应用程序安装目录:
ApplicationData appdata = Windows.Storage.ApplicationData.Current
获取本地存储目录和临时目录:
var localPath = Windows.Storage.ApplicationData.Current.LocalFolder.Path
var tempPath = Windows.Storage.ApplicationData.Current.TemporaryFolder.Path
目录一般安装位置:
"C:\\Users\\{用户名}\\AppData\\Local\\Packages\\{程序GUID}
还有其它一些语言处理等 API,使用商场应用模式是挺方便的。
接下来说一下自定义打包模式,就是直接编译生成一堆文件,然后直接启动 exe 就能运行的,不需要安装。如果想做成安装包,可以先发布,然后使用打包工具打包。
就是在项目文件中加上这两句即可:
<WindowsPackageType>None</WindowsPackageType>
<WindowsAppSDKSelfConatined>true</WindowsAppSDKSelfConatined>
之后会直接生成可执行文件,不再需要安装 MAUI 应用才行运行起来,也不需要证书才能运行。
为 MAUI Blazor 设置语言
MAUI Blazor 在 Windows 上使用的是 WebView2,MAUI Blazor 运行环境是跟程序没关系的,即使是系统设置了中文语言,程序集设置了中文,本地文化设置了中文,CultureInfo 设置了中文,统统都没有用
。
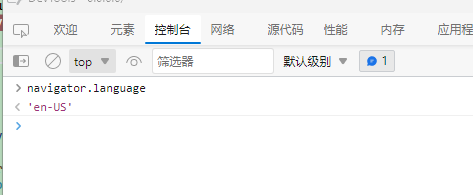
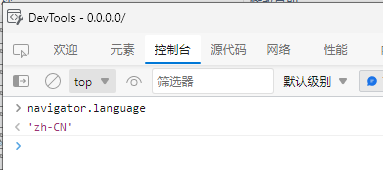
You can check the browser's runtime environment language by pressing F12 after starting the program and executing the following JavaScript code:
navigator.language
'en-US'
Or use the API:
// using Windows.Globalization
var langs = ApplicationLanguages.Languages.ToList<string>();
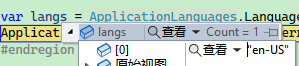
Pitfall ①
First, set Windows.Globalization:
ApplicationLanguages.PrimaryLanguageOverride = "zh-CN";
Then restart the program and notice:
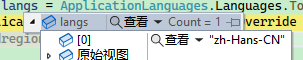
However, the browser language environment remains unchanged:

The reason is that the
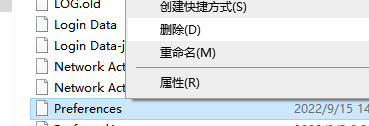
Preferencesfile needs to be regenerated to take effect, which will be mentioned later.
Pitfall ②
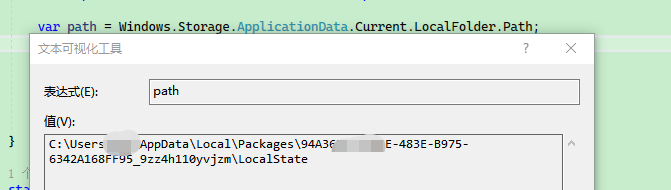
After the program starts, some WebView2 files are generated under {Windows Program Data Directory}/{Your Program ID}/LocalState\EBWebView\Default, including the Preferences file which configures WebView2 parameters.
Find your program data directory:
var path = Windows.Storage.ApplicationData.Current.LocalFolder.Path;
Therefore, you can manually modify the file to allow WebView2 to use the Chinese environment.

var langs = ApplicationLanguages.Languages.ToList<string>();
var cultureInfo = CultureInfo.InstalledUICulture;
var index = langs.FindIndex((lang) => cultureInfo.Equals(CultureInfo.CreateSpecificCulture(lang)));
if (index > 0)
{
ApplicationLanguages.PrimaryLanguageOverride = cultureInfo.Name;
// "...this is immediately reflected in the ApplicationLanguages.Languages property."
langs = ApplicationLanguages.Languages.ToList<string>();
}
var selectedLangs = string.Join(",", langs);
// Should check if this is the same as before but...
var preferences = Windows.Storage.ApplicationData.Current.LocalFolder.Path + "\\EBWebView\\Default\\Preferences";
if (File.Exists(preferences))
{
var jsonString = File.ReadAllText(preferences);
var jsonObject = JObject.Parse(jsonString); // using Newtonsoft.JSON
//var intl = jsonObject["intl"];
jsonObject["intl"] = JObject.Parse($@"{{""selected_languages"": ""{selectedLangs}"",""accept_languages"": ""{selectedLangs}""}}");
jsonString = JsonConvert.SerializeObject(jsonObject);
File.WriteAllText(preferences, jsonString);
}
Pitfall ③
Finally, I found that although the idea in ① was correct, the reason it didn't take effect was that the Preferences file needed to be deleted or recreated; as long as Chinese was set before the program started (before WebView was started), it would work.
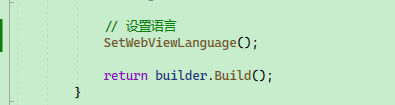
Check the code:
public static class MauiProgram
{
private static void SetWebViewLanguage()
{
ApplicationLanguages.PrimaryLanguageOverride = "zh-CN";
var basePath = Windows.Storage.ApplicationData.Current.LocalFolder.Path;
var preferencesFile = Path.Combine(basePath, "EBWebView/Default/Preferences"); // Preferences
if (!File.Exists(preferencesFile)) return;
var jsonString = File.ReadAllText(preferencesFile);
var jsonObject = JsonObject.Parse(jsonString).AsObject();
var languages = jsonObject["intl"]["selected_languages"].Deserialize<string>() ?? "";
// "zh-CN,en,en-GB,en-US"
if (!languages.StartsWith("zh-CN"))
{
// File.Delete(preferencesFile);
jsonObject.Remove("intl");
jsonObject.Add("intl", JsonObject.Parse("{\"selected_languages\":\"zh-CN,en,en-GB,en-US\"}"));
jsonString = JsonSerializer.Serialize(jsonObject);
File.WriteAllText(preferencesFile, jsonString);
}
}
Use it in public static MauiApp CreateMauiApp():
Configuring the MAUI Project to Start with Administrator Privileges
Background
In Windows, applications can configure what role or permissions to start with using the app.manifest asset file.
The effect is as follows:
Under normal circumstances, adding the following configuration to app.manifest is sufficient:
If this file does not exist in the project, you can create it by adding a new item - Manifest File.
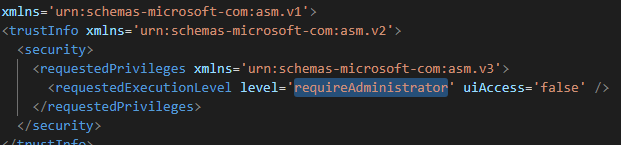
<trustInfo xmlns='urn:schemas-microsoft-com:asm.v2'>
<security>
<requestedPrivileges xmlns='urn:schemas-microsoft-com:asm.v3'>
<requestedExecutionLevel level='requireAdministrator' uiAccess='false' />
</requestedPrivileges>
</security>
</trustInfo>
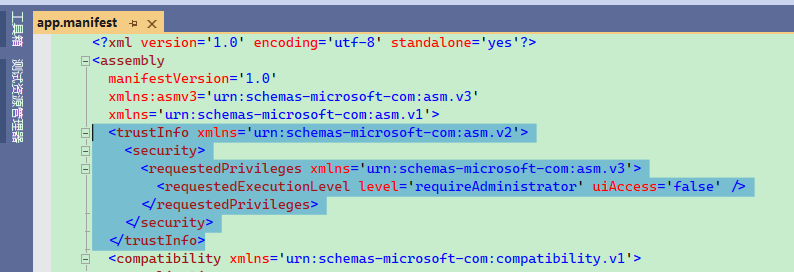
However, in a MAUI application, it cannot be added; if attempted, an error will occur.
Platforms\Windows\app.manifest : manifest authoring error c1010001: Values of attribute "level" not equal in different manifest snippets.
This is because the .NET compiler already generates a default app.manifest file which includes trustInfo configurations.
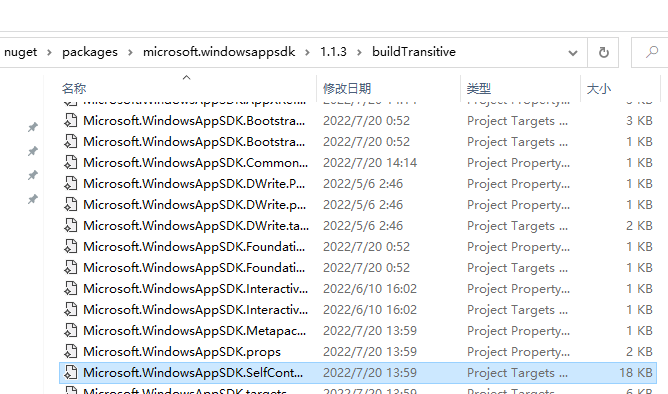
If the project has <WindowsAppSDKSelfContained>true</WindowsAppSDKSelfContained>, you should check the Microsoft.WindowsAppSDK.SelfContained.targets file:
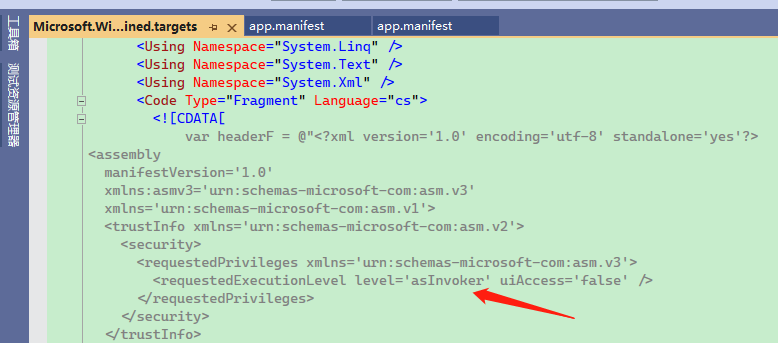
So if you want to customize app.manifest, you have to either modify Microsoft.WindowsAppSDK.SelfContained.targets, but this is not a good approach.
Customizing the Build Process
If you observe the build process, the manifest file will be generated in the obj directory.
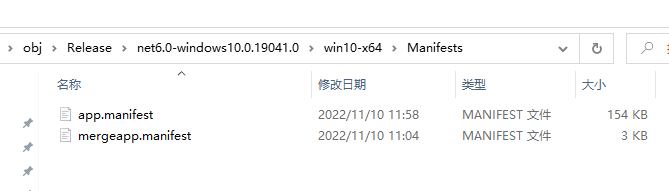
Among them, mergeapp.manifest is the app.manifest from the project, and the .NET compiler renames the developer's file during the build.
During the build, the default app.manifest is first generated from the Microsoft.WindowsAppSDK.SelfContained.targets.
Then the developer's project app.manifest is copied as the mergeapp.manifest, and finally, mergeapp.manifest is merged into app.manifest.
If app.manifest already has configurations, duplicate entries in mergeapp.manifest will result in a build error.
Understanding the build process allows us to manipulate it.
We can replace the configuration in app.manifest before the main program compilation, as follows:
powershell -Command ";(gc app.manifest) -replace 'level=''asInvoker''', 'level=''requireAdministrator''' | Out-File -encoding ASCII app.manifest";
MSBuild build steps can be referred to in the official documentation:
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/visualstudio/msbuild/msbuild-targets?view=vs-2022
There are two important environment variables during the build process:
_DeploymentManifestFiles: Directory of the manifest files;
ApplicationManifest: Path to the app.manifest file.
You can add the following script to the .csproj file, so that the manifest file will be automatically modified during the program build.
<Target Name="RequireAdministrator" BeforeTargets="GenerateManifests" Condition="'$(PublishDir)' != ''">
<Exec WorkingDirectory="./" Command="echo $(ApplicationManifest)" />
<Exec WorkingDirectory="./" Command="echo $(_DeploymentManifestFiles)" />
<Exec WorkingDirectory="$(_DeploymentManifestFiles)" Command="dir" />
<Exec WorkingDirectory="$(_DeploymentManifestFiles)" Command="powershell -Command "(gc app.manifest) -replace 'level=''asInvoker''', 'level=''requireAdministrator''' | Out-File -encoding ASCII app.manifest"" />
</Target>
BeforeTargets="GenerateManifests" indicates that the custom command is executed before GenerateManifests.
Condition="'$(PublishDir)' != ''" indicates the trigger condition; in MAUI, this variable is only populated when publishing, and can be modified to Condition="'$(Release)' != ''".
Note that in some cases, the _DeploymentManifestFiles directory may not exist, so multiple tests may be needed.
Of course, the safest method is:
<Target Name="RequireAdministrator" BeforeTargets="GenerateManifests" Condition="'$(PublishDir)' != ''">
<Exec WorkingDirectory="./" Command=" powershell -Command "(gc $(ApplicationManifest)) -replace 'level=''asInvoker''', 'level=''requireAdministrator''' | Out-File -encoding UTF8 $(ApplicationManifest)"" />
</Target>
The build process mainly involves the following three steps, among which only GenerateManifests can be used in the .csproj file.
<Target Name="GenerateManifests"
Condition="'$(GenerateClickOnceManifests)'=='true' or '@(NativeReference)'!='' or '@(ResolvedIsolatedComModules)'!='' or '$(GenerateAppxManifest)' == 'true'"
DependsOnTargets="$(GenerateManifestsDependsOn)"/>
===================================================
GenerateApplicationManifest
Generates a ClickOnce or native application manifest.
An application manifest specifies declarative application identity, dependency and security information.
===================================================
<Target Name="GenerateApplicationManifest"
DependsOnTargets="
_DeploymentComputeNativeManifestInfo;
_DeploymentComputeClickOnceManifestInfo;
ResolveComReferences;
ResolveNativeReferences;
_GenerateResolvedDeploymentManifestEntryPoint"
Inputs="
$(MSBuildAllProjects);
@(AppConfigWithTargetPath);
$(_DeploymentBaseManifest);
@(ResolvedIsolatedComModules);
@(_DeploymentManifestDependencies);
@(_DeploymentResolvedManifestEntryPoint);
@(_DeploymentManifestFiles)"
Outputs="@(ApplicationManifest)">
Available parameters:
$(_DeploymentBaseManifest);
@(ResolvedIsolatedComModules);
@(_DeploymentManifestDependencies);
@(_DeploymentResolvedManifestEntryPoint);
@(_DeploymentManifestFiles)
@(ApplicationManifest)
MAUI Implementation of Frontend and Backend Separation Development
Background
Initially, the development used Maui + Blazor, leveraging the popular community Blazor UI framework.
However, during the development process, there were many issues with Maui, and the Blazor UI framework also posed several challenges. The pages and styles written with Blazor UI did not pass the scrutiny of designers and product managers.
Ultimately, it was decided to use a native front end in combination with generating static content to be placed in Maui, effectively integrating and packaging the two.
Start with the Frontend
For the frontend, it's a matter of following a normal development pattern without polluting the frontend code.
You can create the frontend project within Visual Studio and place it into the solution, or you can create a separate directory and put the frontend code inside.
Create a MAUI Blazor Project
Create a MAUI Blazor project, the solution is shown below:
First, move the wwwroot/css/app.css file out into wwwroot, and then create a new app.js, also placing it in wwwroot.
Delete the contents of app.css that are unrelated to Blazor, retaining only the following:
#blazor-error-ui {
background: lightyellow;
bottom: 0;
box-shadow: 0 -1px 2px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.2);
display: none;
left: 0;
padding: 0.6rem 1.25rem 0.7rem 1.25rem;
position: fixed;
width: 100%;
z-index: 1000;
}
#blazor-error-ui .dismiss {
cursor: pointer;
position: absolute;
right: 0.75rem;
top: 0.5rem;
}
.blazor-error-boundary {
background: url(data:image/svg+xml;base64,PHN2ZyB3aWR0aD0iNTYiIGhlaWdodD0iNDkiIHhtbG5zPSJodHRwOi8vd3d3LnczLm9yZy8yMDAwL3N2ZyIgeG1sbnM6eGxpbms9Imh0dHA6Ly93d3cudzMub3JnLzE5OTkveGxpbmsiIG92ZXJmbG93PSJoaWRkZW4iPjxkZWZzPjxjbGlwUGF0aCBpZD0iY2xpcDAiPjxyZWN0IHg9IjIzNSIgeT0iNTEiIHdpZHRoPSI1NiIgaGVpZ2h0PSI0OSIvPjwvY2xpcFBhdGg+PC9kZWZzPjxnIGNsaXAtcGF0aD0idXJsKCNjbGlwMCkiIHRyYW5zZm9ybT0idHJhbnNsYXRlKC0yMzUgLTUxKSI+PHBhdGggZD0iTTI2My41MDYgNTFDMjY0LjcxNyA1MSAyNjUuODEzIDUxLjQ4MzcgMjY2LjYwNiA1Mi4yNjU4TDI2Ny4wNTIgNTIuNzk4NyAyNjcuNTM5IDUzLjYyODMgMjkwLjE4NSA5Mi4xODMxIDI5MC41NDUgOTIuNzk1IDI5MC42NTYgOTIuOTk2QzI5MC44NzcgOTMuNTEzIDI5MSA5NC4wODE1IDI5MSA5NC42NzgyIDI5MSA5Ny4wNjUxIDI4OS4wMzggOTkgMjg2LjYxNyA5OUwyNDAuMzgzIDk5QzIzNy45NjMgOTkgMjM2IDk3LjA2NTEgMjM2IDk0LjY3ODIgMjM2IDk0LjM3OTkgMjM2LjAzMSA5NC4wODg2IDIzNi4wODkgOTMuODA3MkwyMzYuMzM4IDkzLjAxNjIgMjM2Ljg1OCA5Mi4xMzE0IDI1OS40NzMgNTMuNjI5NCAyNTkuOTYxIDUyLjc5ODUgMjYwLjQwNyA1Mi4yNjU4QzI2MS4yIDUxLjQ4MzcgMjYyLjI5NiA1MSAyNjMuNTA2IDUxWk0yNjMuNTg2IDY2LjAxODNDMjYwLjczNyA2Ni4wMTgzIDI1OS4zMTMgNjcuMTI0NSAyNTkuMzEzIDY5LjMzNyAyNTkuMzEzIDY5LjYxMDIgMjU5LjMzMiA2OS44NjA4IDI1OS4zNzEgNzAuMDg4N0wyNjEuNzk1IDg0LjAxNjEgMjY1LjM4IDg0LjAxNjEgMjY3LjgyMSA2OS43NDc1QzI2Ny44NiA2OS43MzA5IDI2Ny44NzkgNjkuNTg3NyAyNjcuODc5IDY5LjMxNzkgMjY3Ljg3OSA2Ny4xMTgyIDI2Ni40NDggNjYuMDE4MyAyNjMuNTg2IDY2LjAxODNaTTI2My41NzYgODYuMDU0N0MyNjEuMDQ5IDg2LjA1NDcgMjU5Ljc4NiA4Ny4zMDA1IDI1OS43ODYgODkuNzkyMSAyNTkuNzg2IDkyLjI4MzcgMjYxLjA0OSA5My41Mjk1IDI2My41NzYgOTMuNTI5NSAyNjYuMTE2IDkzLjUyOTUgMjY3LjM4NyA5Mi4yODM3IDI2Ny4zODcgODkuNzkyMSAyNjcuMzg3IDg3LjMwMDUgMjY2LjExNiA4Ni4wNTQ3IDI2My41NzYgODYuMDU0N1oiIGZpbGw9IiNGRkU1MDAiIGZpbGwtcnVsZT0iZXZlbm9kZCIvPjwvZz48L3N2Zz4=) no-repeat 1rem/1.8rem, #b32121;
padding: 1rem 1rem 1rem 3.7rem;
color: white;
}
.blazor-error-boundary::after {
content: "An error has occurred."
}
.status-bar-safe-area {
display: none;
}
@supports (-webkit-touch-callout: none) {
.status-bar-safe-area {
display: flex;
position: sticky;
top: 0;
height: env(safe-area-inset-top);
background-color: #f7f7f7;
width: 100%;
z-index: 1;
}
.flex-column, .navbar-brand {
padding-left: env(safe-area-inset-left);
}
}
Next, place the following code into app.js to dynamically import the frontend-generated CSS files.
function InitializeCss(name) {
document.getElementById("app-css").innerHTML = '<link rel="stylesheet" href="' + name + '">';
}
Then delete the js and css directories.
The remaining files are shown in the image:
Then modify index.html, with the content as follows:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0, maximum-scale=1.0, user-scalable=no, viewport-fit=cover" />
<title>MauiApp3</title>
<base href="/" />
<link href="/app.css" rel="stylesheet" />
</head>
<body>
<div id="app-css"></div>
<div class="status-bar-safe-area"></div>
<div id="app">Loading...</div>
<div id="blazor-error-ui">
An unhandled error has occurred.
<a href="" class="reload">Reload</a>
<a class="dismiss">🗙</a>
</div>
<script src="app.js"></script>
<script src="_framework/blazor.webview.js" autostart="false"></script>
</body>
</html>
The added <div id="app-css"></div> is used for dynamically loading CSS files.
Other content remains mostly unchanged.
Open MainLayout.razor, which is responsible for dynamically loading frontend files; its contents are as follows:
@using MauiApp3.Data
@inherits LayoutComponentBase
@code {
#region static fields
private static readonly string[] css;
private static readonly string[] js;
#endregion
#region instance fields
[Inject]
private IJSRuntime JS { get; set; }
#endregion
static MainLayout()
{
var path = Windows.ApplicationModel.Package.Current.InstalledLocation.Path;
if (Directory.Exists(Path.Combine(path, "wwwroot", "css")))
{
var cssList = Directory.GetFiles(Path.Combine(path, "wwwroot", "css"))
.Where(x => x.EndsWith(".css"))
.Select(x => Path.GetFileName(x)).ToArray();
css = cssList;
}
else css = Array.Empty<string>();
if (Directory.Exists(Path.Combine(path, "wwwroot", "js")))
{
var jsList = Directory.GetFiles(Path.Combine(path, "wwwroot", "js"))
.Where(x => x.EndsWith(".js"))
.Select(x => Path.GetFileName(x)).ToArray();
js = jsList;
}
else js = Array.Empty<string>();
}
protected override async Task OnInitializedAsync()
{
await Task.CompletedTask;
}
protected override async Task OnAfterRenderAsync(bool firstRender)
{
if (firstRender)
{
foreach (var item in css)
{
await JS.InvokeVoidAsync("InitializeCss", $"css/{item}");
}
foreach (var item in js)
{
await JS.InvokeAsync<IJSObjectReference>("import", $"/js/{item}");
}
}
}
}
Then, to automatically copy the generated frontend content into Maui, you can set up a script in Maui's .csproj file, adding the following content:
<Target Name="ClientBuild" BeforeTargets="BeforeBuild">
<Exec WorkingDirectory="../vueproject1" Command="npm install" />
<Exec WorkingDirectory="../vueproject1" Command="npm run build" />
<Exec WorkingDirectory="../vueproject1" Command="DEL "dist\index.html"" />
<Exec WorkingDirectory="./" Command="RMDIR /s/q "css"" />
<Exec WorkingDirectory="./" Command="RMDIR /s/q "js"" />
<Exec WorkingDirectory="../vueproject1" Command="Xcopy "dist" "../MauiApp3/wwwroot" /E/C/I/Y" />
<Exec WorkingDirectory="./" Command="RMDIR /s/q "$(LayoutDir)""/>
</Target>

Thus, when the Maui project starts, it will compile the frontend project and then copy the generated files (excluding index.html) to the wwwroot directory.
After starting:
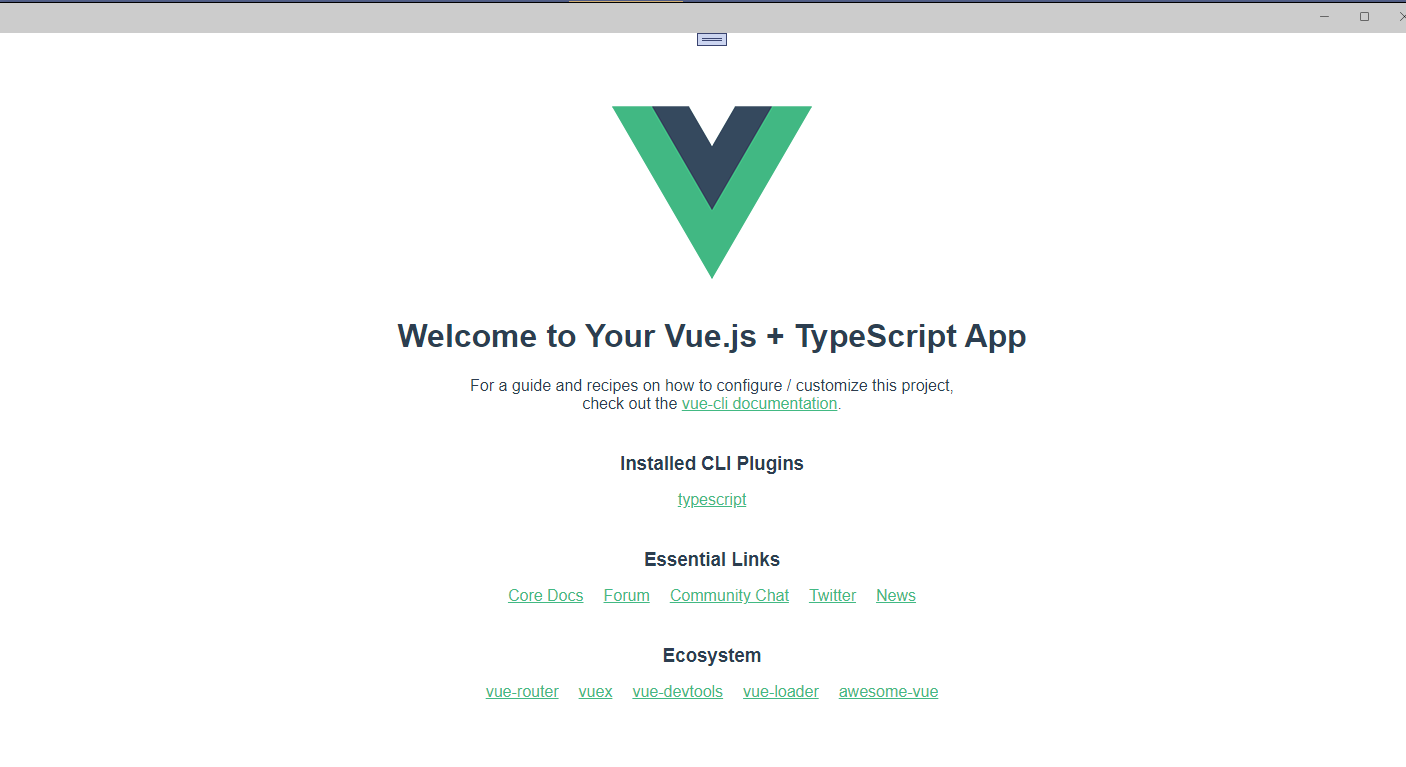
C# Automated Certificate Generation, Local Certificate Installation, and Solving Certificate Trust Issues
Background
When developing Blazor, the environment is https://0.0.0.0/, meaning that MAUI Blazor can only send HTTPS requests; it cannot send HTTP requests or insecure HTTPS requests. However, internal network HTTPS is not considered secure.
。
Therefore, a local proxy service needs to be implemented, allowing the application to access via HTTPS. To ensure HTTPS security, automated certificate installation is required.
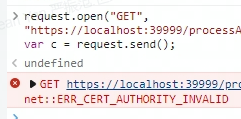
This can lead to issues where JavaScript cannot send requests. To secure HTTPS, the process for automatically generating and installing certificates locally on localhost is implemented.
Code Implementation
The certificate generation utilizes the built-in libraries from .NET, without requiring third-party packages.
using System.Security.Cryptography;
using System.Security.Cryptography.X509Certificates;
using System.Text;
The method for generating certificates references the project https://github.com/dotnetcore/FastGithub.
The first step is to write a certificate generator, which includes code directly copied from here: https://github.com/dotnetcore/FastGithub/blob/9f9cbce624310c207b01699de2a5818a742e11ca/FastGithub.HttpServer/Certs/CertGenerator.cs
Next, define the service managing the generated certificates. The original author used .NET 7, but since the current stable version is .NET 6 and many APIs are unavailable, modifications are necessary. The original location is:
https://github.com/dotnetcore/FastGithub/blob/9f9cbce624310c207b01699de2a5818a742e11ca/FastGithub.HttpServer/Certs/CertService.cs
Define the locations and names of the certificates:
private const string CACERT_PATH = "cacert";
/// <summary>
/// Get the certificate file path
/// </summary>
public string CaCerFilePath { get; } = OperatingSystem.IsLinux() ? $"{CACERT_PATH}/https.crt" : $"{CACERT_PATH}/https.cer";
/// <summary>
/// Get the private key file path
/// </summary>
public string CaKeyFilePath { get; } = $"{CACERT_PATH}/https.key";
This involves two files: the client certificate and the private key.
.key is the private key, which can be used to generate the server and client certificates; thus, only the .key private key needs to be saved without exporting the server certificate.
.csr, .cer are the client certificates, and on Windows, the .cer format can be used. The reason for exporting the client certificate is for installing the certificate once, without needing to generate it dynamically.
The rules for the certificate management service state that if there are no certificates in the ssl directory, then it will generate and install them; if the files already exist, it loads them into memory without reinstalling.
The complete code is as follows:
/// <summary>
/// Certificate generation service
/// </summary>
internal class CertService
{
private const string CACERT_PATH = "cacert";
/// <summary>
/// Get the certificate file path
/// </summary>
public string CaCerFilePath { get; } = OperatingSystem.IsLinux() ? $"{CACERT_PATH}/https.crt" : $"{CACERT_PATH}/https.cer";
/// <summary>
/// Get the private key file path
/// </summary>
public string CaKeyFilePath { get; } = $"{CACERT_PATH}/https.key";
private X509Certificate2? caCert;
/*
Locally generates cer and key files; the cer file is imported into the Windows certificate manager.
The key file is used to generate X509 certificate on each startup for the web service.
*/
/// <summary>
/// Generate CA certificate if it does not exist
/// </summary>
public bool CreateCaCertIfNotExists()
{
if (!Directory.Exists(CACERT_PATH)) Directory.CreateDirectory(CACERT_PATH);
if (File.Exists(this.CaCerFilePath) && File.Exists(this.CaKeyFilePath))
{
return false;
}
File.Delete(this.CaCerFilePath);
File.Delete(this.CaKeyFilePath);
var notBefore = DateTimeOffset.Now.AddDays(-1);
var notAfter = DateTimeOffset.Now.AddYears(10);
var subjectName = new X500DistinguishedName($"CN=运连网物流管理系统");
this.caCert = CertGenerator.CreateCACertificate(subjectName, notBefore, notAfter);
var privateKeyPem = ExportRSAPrivateKeyPem(this.caCert.GetRSAPrivateKey());
File.WriteAllText(this.CaKeyFilePath, new string(privateKeyPem), Encoding.ASCII);
var certPem = ExportCertificatePem(this.caCert);
File.WriteAllText(this.CaCerFilePath, new string(certPem), Encoding.ASCII);
return true;
}
/// <summary>
/// Get the certificate issued to the specified domain
/// </summary>
/// <param name="domain"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public X509Certificate2 GetOrCreateServerCert(string? domain)
{
if (this.caCert == null)
{
using var rsa = RSA.Create();
rsa.ImportFromPem(File.ReadAllText(this.CaKeyFilePath));
this.caCert = new X509Certificate2(this.CaCerFilePath).CopyWithPrivateKey(rsa);
}
var key = $"{nameof(CertService)}:{domain}";
var endCert = GetOrCreateCert();
return endCert!;
// Generate a one-year certificate for the domain
X509Certificate2 GetOrCreateCert()
{
var notBefore = DateTimeOffset.Now.AddDays(-1);
var notAfter = DateTimeOffset.Now.AddYears(1);
var extraDomains = GetExtraDomains();
var subjectName = new X500DistinguishedName($"CN={domain}");
var endCert = CertGenerator.CreateEndCertificate(this.caCert, subjectName, extraDomains, notBefore, notAfter);
// Reinitialize the certificate to accommodate Windows platform's inability to use in-memory certificates
return new X509Certificate2(endCert.Export(X509ContentType.Pfx));
}
}
private static IEnumerable<string> GetExtraDomains()
{
yield return Environment.MachineName;
yield return IPAddress.Loopback.ToString();
yield return IPAddress.IPv6Loopback.ToString();
}
internal const string RasPrivateKey = "RSA PRIVATE KEY";
private static string ExportRSAPrivateKeyPem(RSA rsa)
{
var key = rsa.ExportRSAPrivateKey();
var chars = PemEncoding.Write(RasPrivateKey, key);
return new string(chars);
}
private static string ExportCertificatePem(X509Certificate2 x509)
{
var chars = PemEncoding.Write(PemLabels.X509Certificate, x509.Export(X509ContentType.Cert));
return new string(chars);
}
/// <summary>
/// Install CA certificate
/// </summary>
/// <exception cref="Exception">Cannot install certificate</exception>
public void Install( )
{
var caCertFilePath = CaCerFilePath;
try
{
using var store = new X509Store(StoreName.Root, StoreLocation.LocalMachine);
store.Open(OpenFlags.ReadWrite);
var caCert = new X509Certificate2(caCertFilePath);
var subjectName = caCert.Subject[3..];
foreach (var item in store.Certificates.Find(X509FindType.FindBySubjectName, subjectName, false))
{
if (item.Thumbprint != caCert.Thumbprint)
{
store.Remove(item);
}
}
if (store.Certificates.Find(X509FindType.FindByThumbprint, caCert.Thumbprint, true).Count == 0)
{
store.Add(caCert);
}
store.Close();
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
throw new Exception($"Please manually install the CA certificate {caCertFilePath} into 'Place all certificates in the following store'\\'Trusted Root Certification Authorities'" + ex);
}
}
}
}
Using in ASP.NET Core
In ASP.NET Core, load the server certificate (generating X509 certificates on each startup).
var sslService = new CertService();
if(sslService.CreateCaCertIfNotExists())
{
try
{
sslService.Install();
}
catch (Exception)
{
}
}
var webhost = WebHost.CreateDefaultBuilder()
.UseStartup<Startup>()
.UseKestrel(serverOptions =>
{
serverOptions.ListenAnyIP(39999,
listenOptions =>
{
var certificate = sslService.GetOrCreateServerCert("localhost");
listenOptions.UseHttps(certificate);
});
})
.Build();
await webhost.RunAsync();

文章评论