问题背景
在 Windows 中,开发的应用可以使用 app.manifest 资产文件配置程序启动时,使用何种角色权限启动。
效果如下:
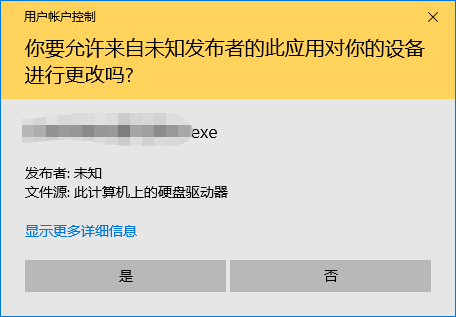
正常情况下,在 app.manifest 加上以下配置即可:
如果项目中没有这个文件,可以在项目中新建项-清单文件。
<trustInfo xmlns='urn:schemas-microsoft-com:asm.v2'>
<security>
<requestedPrivileges xmlns='urn:schemas-microsoft-com:asm.v3'>
<requestedExecutionLevel level='requireAdministrator' uiAccess='false' />
</requestedPrivileges>
</security>
</trustInfo>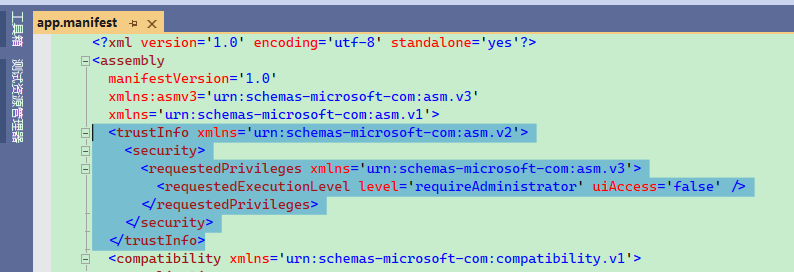
但是在 MAUI 应用中,是加不上去的,如果加上去,就会出现报错。
Platforms\Windows\app.manifest : manifest authoring error c1010001: Values of attribute "level" not equal in different manifest snippets. 因为 .NET 编译器中,已经默认为程序生成一个 app.manifest 文件,其文件内容中已经包含了 trustInfo 配置。
如果项目中开启了 <WindowsAppSDKSelfConatined>true</WindowsAppSDKSelfConatined>,那么应该查看 Microsoft.WindowsAppSDK.SelfContained.targets 文件:
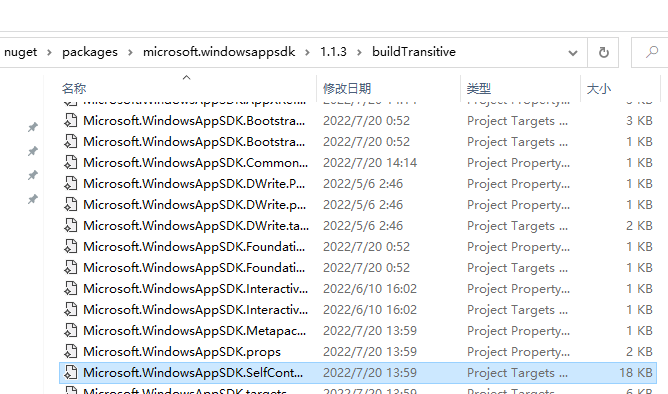
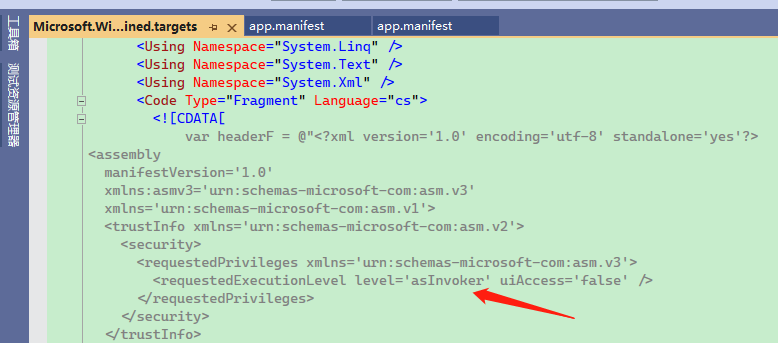
所以如果要自定义 app.manifest ,要么就是把 Microsoft.WindowsAppSDK.SelfContained.targets 改了,但是这样不太好。
定制编译过程
如果观察编译过程,会发现 manifest 文件会生成到 obj 目录。
其中 mergeapp.manifest 便是项目中的 app.manifest ,.NET 编译的时候将开发者的文件改名字了。
程序编译时,首先从 Microsoft.WindowsAppSDK.SelfContained.targets 中生成默认的 app.manifest。
接着将开发者项目中的 app.manifest 复制为 mergeapp.manifest 文件,然后将 mergeapp.manifest 合并到 app.manifest。
如果 app.manifest 中已经存在配置,那么 mergeapp.manifest 中重复的记录就会导致编译报错。
既然了解到了编译过程,那么我们可以在编译过程中做手脚。
我们可以在编译生成 app.manifest 但是还没有编译主程序的时候,将 app.manifest 中的配置替换掉,替换命令是:
powershell -Command ";(gc app.manifest) -replace 'level=''asInvoker''', 'level=''requireAdministrator''' | Out-File -encoding ASCII app.manifest";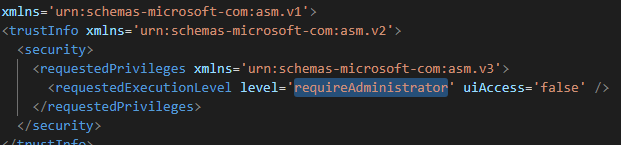
MSBuild 编译使用到的步骤可以参考官方文档:
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/visualstudio/msbuild/msbuild-targets?view=vs-2022
在编译过程中,有两个重要的环境变量:
_DeploymentManifestFiles :清单文件所在目录;
ApplicationManifest: app.manifest 文件路径。
可以在 .csproj 文件中加入以下脚本,这样会在程序编译时,自动修改清单文件。
<Target Name="RequireAdministrator" BeforeTargets="GenerateManifests" Condition="'$(PublishDir)' != ''">
<Exec WorkingDirectory="./" Command="echo $(ApplicationManifest)" />
<Exec WorkingDirectory="./" Command="echo $(_DeploymentManifestFiles)" />
<Exec WorkingDirectory="$(_DeploymentManifestFiles)" Command="dir" />
<Exec WorkingDirectory="$(_DeploymentManifestFiles)" Command="powershell -Command "(gc app.manifest) -replace 'level=''asInvoker''', 'level=''requireAdministrator''' | Out-File -encoding ASCII app.manifest"" />
</Target> BeforeTargets="GenerateManifests" 表明在 GenerateManifests 之前,执行里面的自定义命令。
Condition="'$(PublishDir)' != ''" 表示触发条件,在 MAUI 中,只有发布的时候才会有这个变量,也可以改成 Condition="'$(Release)' != ''"。
注意,有些情况下 _DeploymentManifestFiles 目录会不存在,因此可以多次测试一下。
当然,最保险的方法:
<Target Name="RequireAdministrator" BeforeTargets="GenerateManifests" Condition="'$(PublishDir)' != ''">
<Exec WorkingDirectory="./" Command=" powershell -Command "(gc $(ApplicationManifest)) -replace 'level=''asInvoker''', 'level=''requireAdministrator''' | Out-File -encoding UTF8 $(ApplicationManifest)"" />
</Target>编译过程主要在以下三步,其中只有 GenerateManifests 能够在 .csproj 中使用。
<Target Name="GenerateManifests"
Condition="'$(GenerateClickOnceManifests)'=='true' or '@(NativeReference)'!='' or '@(ResolvedIsolatedComModules)'!='' or '$(GenerateAppxManifest)' == 'true'"
DependsOnTargets="$(GenerateManifestsDependsOn)"/>
===================================================
GenerateApplicationManifest
Generates a ClickOnce or native application manifest.
An application manifest specifies declarative application identity, dependency and security information.
===================================================
<Target Name="GenerateApplicationManifest"
DependsOnTargets="
_DeploymentComputeNativeManifestInfo;
_DeploymentComputeClickOnceManifestInfo;
ResolveComReferences;
ResolveNativeReferences;
_GenerateResolvedDeploymentManifestEntryPoint"
Inputs="
$(MSBuildAllProjects);
@(AppConfigWithTargetPath);
$(_DeploymentBaseManifest);
@(ResolvedIsolatedComModules);
@(_DeploymentManifestDependencies);
@(_DeploymentResolvedManifestEntryPoint);
@(_DeploymentManifestFiles)"
Outputs="@(ApplicationManifest)">能够拿到参数:
$(_DeploymentBaseManifest);
@(ResolvedIsolatedComModules);
@(_DeploymentManifestDependencies);
@(_DeploymentResolvedManifestEntryPoint);
@(_DeploymentManifestFiles)
@(ApplicationManifest)
文章评论